Retinol
Retinol is THE anti-aging vitamin. But did you know that it is also used to treat acne? Here’s all you need to know about this powerhouse ingredient.
Before we take a closer look at the anti-aging ingredient and its effects, we must first understand how it works and what retinol actually is. Let’s start with the fact that retinol belongs to the retinoids. This group includes all derivatives of vitamin A.
The most active form of vitamin A is vitamin A acid (retinoic acid, tretinoin). However, it is only available on prescription and therefore can’t be used by cosmetic manufacturers. The reason for this is that although retinoic acid is extremely effective against acne, it can often lead to adverse side effects like skin irritation and should therefore only be prescribed under medical supervision. Over-the-counter retinol serums or creams usually contain vitamin A derivatives instead. Those are much more gentle on the skin, yet still very effective. There are different forms that can be used, but they also differ in effect. However, other factors can also influence the effect on the skin; it also depends on which other active ingredients are added to a product, for example. Read more to learn more about the difference between retinol, retinal and other retinoids and how to find the best product for your skin.
The effect of each vitamin A derivative unfolds when it is applied to the skin and converted into the active form, vitamin A acid (=retinoic acid). As you recall, retinoic acid is the original form. The fewer conversion steps a retinoid needs, the more potent it is.
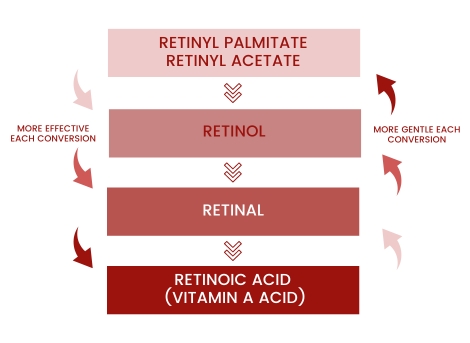

Retinoids that require fewer conversion steps also carry a higher risk of irritation than forms of vitamin A that absorb slower into the skin.
Retinyl palmitate and Retinyl acetate, for example, are widely used in various cosmetic products. Both require several conversion steps, but are very well tolerated compared to others.
Retinal is a precursor of retinoic acid and needs just one conversion step to be active in the skin. Retinol itself is the chemical precursor of retinal and thus needs only two conversion steps. This makes both types very effective and they can deliver visible results after the very first application. However, they also come with a higher risk of irritation. Users that are inexperienced with active ingredients or have very sensitive skin may initially experience side effects like itching or redness.
Retinoids that require fewer conversion steps also carry a higher risk of irritation than forms of vitamin A that absorb slower into the skin.
Retinyl palmitate and Retinyl acetate, for example, are widely used in various cosmetic products. Both require several conversion steps, but are very well tolerated compared to others.
Retinal is a precursor of retinoic acid and needs just one conversion step to be active in the skin. Retinol itself is the chemical precursor of retinal and thus needs only two conversion steps. This makes both types very effective and they can deliver visible results after the very first application. However, they also come with a higher risk of irritation. Users that are inexperienced with active ingredients or have very sensitive skin may initially experience side effects like itching or redness.
As a general rule:
Beginner retinol users are advised to start slowly and increase the use of retinol products gradually.
What Does Retinol Do
- Anti-aging effect: Reduction of fine lines and wrinkles
- Promotes skin renewal and tightens the skin
- Fights free radicals
- Improves skin texture and provides antibacterial properties
- Boosts the formation of new cells and skin regeneration
- Stimulates collagen production
- Reduces dark spots
Apropos, free radicals are one of the triggers of premature skin aging. They are created by the body in normal metabolic processes and by external influences such as UV rays.
How to Use Retinol Correctly


1. It is better to apply serums with a high concentration of retinol in the evening. This is because it makes the skin more sensitive to sun damage, which is why you should use sunscreen (at least SPF 30) the next day.

2. Start slowly. The skin may react differently depending on the type of retinol you use. At first, you may experience an overdose, the so-called ‘retinol burn‘, where the skin reacts with irritation or itching. To prevent this, you can simply increase the dosage gradually. Once your skin has become accustomed to the powerful effects of retinol, you can achieve quick and visible results.


3. Do not use retinol products during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.

4. Do not combine retinol with chemical peels on the same day, as this can lead to irritation. Chemical peels include AHA, BHA (salicylic acid) and PHA products. However, if you alternate between the two every other day, they work very well together.
Effective Combinations of Active Ingredients
Finding the right combination will lead to the best results! Vitamin C or niacinamide are perfect additions to your skincare routine! Our tip: Use a vitamin C serum in the morning and your retinol serum in the evening to achieve effective anti-aging results. You want to improve your skin tone and texture? Then products with niacinamide (vitamin B3) are ideal. Simply apply these before the retinol product. It is important that you always finish your beauty routine with your usual moisturizer after using a retinol serum.
Some active ingredients that you can always add to your skincare routine: Hyaluronic acid provides great anti-wrinkle and hydrating properties for dry skin, while vitamin E is an excellent free radical scavenger. Ceramide, squalane and nourishing lipids strengthen the skin barrier and promote a long-lasting improvement for all skin types.
Did you know that there are even maritime ingredients that act just like vitamin A? This includes, for example, the sea fennel.
Who Should Use Retinol?
One thing is clear. Retinol is much more than just a great anti-aging ingredient. It is actually very versatile. The following skin types and skin concerns benefit greatly from using retinoids.
- Fine lines and wrinkles
- Combination skin
- Pimple marks
- Oily skin
- Blemish-prone and acne-prone skin
- Skin prone to hyperpigmentation, brown spots
Who Should Use Retinol?
One thing is clear. Retinol is much more than just a great anti-aging ingredient. It is actually very versatile. The following skin types and skin concerns benefit greatly from using retinoids.
- Fine lines and wrinkles
- Combination skin
- Pimple marks
- Oily skin
- Blemish-prone and acne-prone skin
- Skin prone to hyperpigmentation, brown spots